Statistics show that 97% of companies that implemented best-in-class forecasting processes achieved quotas, compared to 55% that didn’t. At the same time, companies with accurate forecasts are 10% more likely to grow revenue year-over-year and twice as likely to be at the top of their field.
I’m not going to ask you whether or not you’d like to be among the top of the field companies. Of course you would.
Unfortunately it’s not that easy. According to statistics, 55% of sales leaders do not have high confidence in their forecasting accuracy; a whopping 67% of organisations lack a formalised approach to forecasting altogether.
Don’t get discouraged, though! NetHunt is ready to give you a helping hand. We’ve prepared all the answers to the whats, whys and hows of sales forecasting using the CRM data to plant your business among that successful 45%.
What is sales forecasting?
Just like a business plan or a development strategy, sales forecasting is an integral component of any business. It’s a prediction of the number of deals that you will be able to close within a given timeframe. You can calculate a sales forecast for your team, the whole company, or each individual salesperson depending on their past performance. Remember, forecasting doesn't mean fortune-telling.
To achieve high sales forecast accuracy, businesses use resource available to them such as historical data, experience gained from internal and external factors, as well as your sales reps’ expertise to make an estimate of how much your business will sell over a specific period in the future.
Why is sales forecasting important?
While some sales managers neglect forecasting their sales, the truth is it may greatly benefit your business and give some unexpected insights into the sales process. Sales forecasting is essential for sales managers to take on for a variety of reasons...
- It helps to make informed decisions.
- It tracks sales performance.
- It motivates target attainment.
- It prompts you to understand customers better.
- It streamlines cash flow, credit, and financing.
Proper sales forecasting will help you set business objectives for the future. You’ll be able to predict not only the number of deals closed along with the revenue they will bring, but also the amount of time needed to achieve your goals. This, in turn, will help you set priorities and organize the work process accordingly.
All in all, sales forecasting aids business growth.
The different types of sales forecasting
Sales forecasting success depends on the method chosen to carry out calculations. There are plenty of different methods that vary in difficulty, requirements, and accuracy. Just pick the approach that suits your business needs.Below we’ve compiled a list of the five most popular and versatile sales forecasting methods for you to use.
Opportunity stage forecasting
The majority of businesses break down their sales pipeline into stages. The naming of these stages depends on business specifics and processes, but essentially all correspond to the following phases of the sales cycle...
- Prospecting
- Qualification
- Nurturing
- Quotation
- Closing
- Deal won/ deal lost
Opportunity stage forecasting assumes that deals have a different likelihood of success at different sales cycle stages. For example, if you know that you typically win about three-quarters of deals that enter the ‘Negotiation’ stage, you can predict to have a 75/25 shot for all the deals in that stage over the given time.
Essentially, the opportunity stage model allows you to calculate the chance of closing each deal, based on where a prospect currently is in your sales cycle. To do that, you need to understand your average sales cycle and map out all the stages that comprise it. Once you have a good grasp of how your target audience behaves at different points of their customer journey - from awareness to purchase - you can estimate the likelihood of winning a deal in the forecasted period. You may calculate a sales forecast including OKRs.
The probability (%) of closing a deal is different for every business; it’s affected by both internal and external factors. Still, you can use the following example as a template for opportunity stage forecasting...
Pipeline stage closure probablities
- Contact information collected - 10%
- Quota requested - 15%
- Appointment scheduled - 20%
- Qualified to buy - 40%
- Hosted demo call - 60%
- Contract sent - 90%
- Deal won - 100%
- Deal lost - 0%
Remember! This forecasting method will only provide accurate predictions, if you have a detailed plan of action regarding what it takes to move the lead from one stage of the sales funnel to another. Unless your customer journey is standardised, the probability of closing a deal will vary greatly from lead to lead. It’ll be very unpredictable.
To calculate your expected revenue for the forecasted period, you need to multiply the deal amount by its closing probability...
Expected revenue =
Deal size x Probability of closing
To estimate the overall forecast revenue, you need to calculate the expected revenue for each deal in the sales pipeline and add them all together. Here’s a simple example of what it would look like...
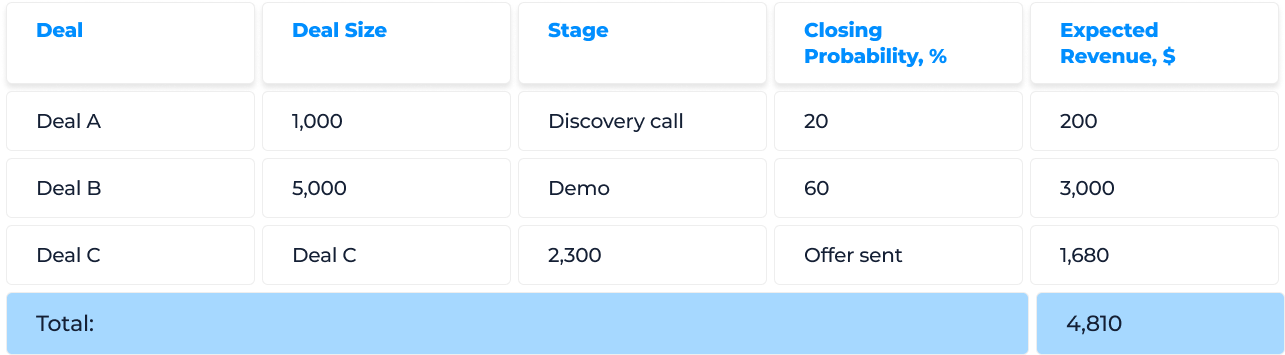
The pros and cons of opportunity stage forecasting
✅ It uses basic maths. You don’t need to be a professional mathematician to carry out the calculations.
✅ It is relatively objective.
❌ It leaves out a lot of factors that impact the likelihood of closing a deal, such as deal age, lead demographics, firmographics, and behaviour.
❌ It’s easy to assign a wrong closing probability to different sales pipeline stages which can mess up the accuracy of the sales forecast.
Opportunity creation forecasting
When you read a detective novel for the first time, it’s unlikely that you’ll guess who the killer is. Unfamiliar with the genre’s cliches, you can’t even predict that it was the butler who did it. However, once you get into it and binge a couple more books, you start noticing patterns and predict the majority of plot twists. You use your past experience, and analyse behaviour and appearance of different characters to forecast the outcome of the story.
Opportunity creation forecasting method uses the same principle. It allows sales managers to predict which opportunities are more likely to close and deal value based on the leads’ demographic, firmographic, and behavioural data.
To create a sales forecast using the opportunity creation method, you’ll need to do the following…
- Analyse all closed deals in CRM to identify their characteristics.
- Create a list of common characteristics; identify which have impact on closing.
- Look for the characteristics you’ve outlined in your current pool of leads.
For more accurate forecasting, combine the characteristic you’ve identified as the most important with the lead score when determining closing probability. Then, use the following formula to calculate the expected value of each opportunity in the sales pipeline...
Expected opportunity value = Average sale price x Average close rate
To calculate the expected revenue for the forecasted period, add all the expected values of each deal in the pipeline.
For example... If you found that the size of the company has the most impact on closing the deal and the majority of your customers are large enterprises, look at this characteristic when forecasting the expected value of the opportunity. Then, look at how leads with different lead scores (high-quality ones and lower-quality ones) that share this characteristic convert to spot a pattern.
The pros and cons of opportunity stage forecasting
✅ It is objective.
✅ It takes a variety of factors into consideration.
✅ It allows prioritising opportunities as it shows their potential.
❌ It's difficult to calculate.
❌ It only works with comprehensive and accurate historical data.
Length of sales cycle forecasting
When forecasting sales with the length of the sales cycle method, sales managers use the average time it takes a lead to convert as a paying customer to identify the deal’s closing probability. For example, if your business’s average sales cycle is four months, a lead that you’ve been nurturing for three months is 75% likely to make a purchase.
This method is relatively objective as it doesn’t rely on the sales rep’s emotions that can spur overly generous predictions. If your sales rep secures a demo call, they might assume that a lead is ready to commit. In reality, the lead has only recently started engaging with your business, so they aren’t ready to buy just yet. This is reflected in the calculations.
One of the biggest advantages of this forecasting method is that you can use it for a multitude of different sales cycles. For instance, you can calculate the expected revenue for both the leads that come from the website, webinars and referrals.
To forecast the expected revenue of each deal, use the following formula...
Expected revenue =
(# days since lead entered sales funnel ÷ Average length of the sales cycle)
x Average close rate
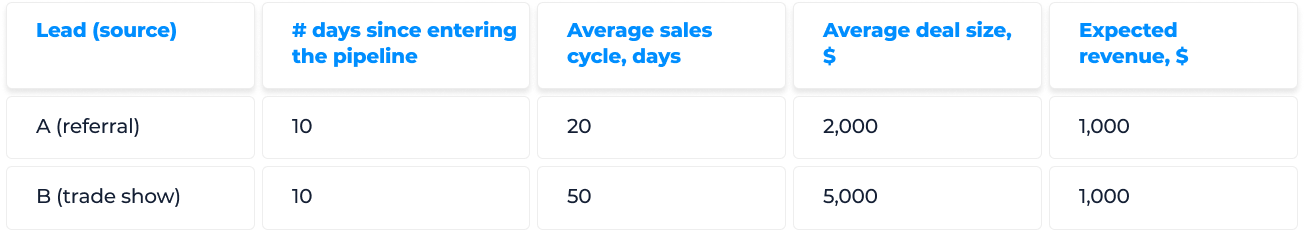
Beware! To use this method, you need to accurately track when and how leads enter your sales pipeline. This is only possible when you use a CRM system that integrates with marketing software, and automatically log every interaction you have with your leads along their journey down the funnel.
The pros and cons of opportunity stage forecasting
✅ It's objective. It doesn’t take the sales rep’s emotions into account.
✅ It can be used for multiple sales cycles.
❌ It only works with carefully tracked, complete data.
❌ It doesn’t consider the size of the deal and other peculiarities.
Intuitive forecasting
The concept of intuitive forecasting method is straightforward. The sales manager simply asks their sales rep to predict the outcome of a specific deal and expects a professional estimate of the situation.
This approach makes a lot of sense when you think about it. You hire professionals for a reason. You want to be able to rely on their expertise. Besides, sales reps are the people who interact with leads. They have a good understanding of who the lead is, what their needs and objections are (if any), and where they stand in the buyer’s journey. Hence, they can give you a pretty accurate estimate of the deal’s closing probability as well as its size.
Intuitive forecasting is one of the only accessible forecasting methods for companies that don’t have any historical data to base their estimates on. However, there are a couple of serious downsides to this method.
Unfortunately, there’s no scalable way to verify intuitive forecasts. Sales reps tend to be overly optimistic about deals. It’s not unusual for them to predict that closing a deal will take less time or that a contract will be larger than it really is. The only way a sales manager can tell whether or not the rep is accurate in their predictions is to go through every call, email, and any other interaction between a lead and the company.
For this method to work as intended, you need a disciplined approach to recording customer data. You need to motivate your sales team to log every interaction in CRM to have access to all the details and offer a more realistic opinion.
The pros and cons of opportunity stage forecasting
✅ It works well for start-up companies that don’t have any historical data to base forecasts on.
✅ It's easy to use.
❌ It's highly subjective. Sales reps tend to be overly optimistic about their sales performance, which can lead to inaccurate predictions.
Historical forecasting
This forecasting method is quick and quite dirty. You simply use the sales pipeline data you already have, put it into a graphic calculator - or any software that offers the same functionality - and extrapolate the trend line.
If you’ve experienced an increase in sales in the previous period, you assume the trend will continue and your sales will grow in the forecasted period too. To calculate expected revenue, you can use the following formula...
Expected revenue =
(Current period revenue ÷ Previous period revenue)
x Current period revenue
Now, historical forecasting is a sticky one. Something as common as market seasonality or something as huge and out of the ordinary as a global pandemic can eff you up big time. This forecasting method doesn’t account for changes in the external environment.
The pros and cons of opportunity stage forecasting
✅ It doesn’t rely on data accuracy as heavily as other methods.
✅ It's easy to use.
❌ It doesn’t account for the seasonality of the market, buyer demand, and other external factors.
❌ It doesn’t take the sales pipeline into consideration.
How to create a sales forecast in NetHunt CRM
We’ve established the fact that the majority of sales forecasting methods require accurate data, so it’s essential that you have a reliable sales CRM solution to store the details of your interactions with leads. However, there’s something else a CRM system can come in handy for - you can use the software to automate sales forecasting.
- Press on the ‘Add new field’ button to create the two necessary fields for your sales forecast: The deal's value or amount (currency); the probability of that deal (percentage).
- After you create the first two fields, you need to create the final one using the formula field and multiply the first two values. Type in the exact field names in the formula as it is shown in the example below the field.
- Create a card view by stage and customise the card layout so that you can see the sales forecast for each of your deals in the pipeline.
- Select the formula field with your forecast to summarise.
Now in your pipeline stages, you should be able to visualize the forecast for each deal as well as the summary for each stage.
With a formalised approach to sales forecasting, you can achieve great results and hit your sales targets. Good luck and let’s get growing!




















 product experts — let's find the best setup for your team
product experts — let's find the best setup for your team